PART 1.1
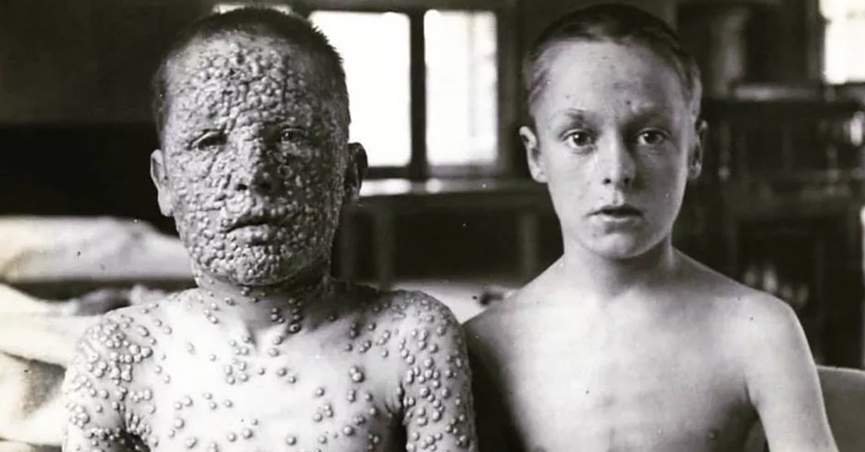
The risk of smallpox was accepted as just an unfortunate part of life. Getting sick was a person’s fate. But in the late 1700s, Dr. Edward Jenner saw things differently and applied a “cause and effect” mindset. After years of observation, he was convinced that having cowpox protected people from contracting smallpox.
PART 1.2
In the early days of HIV/AIDS, AIDS was a mysterious disease. The cause of AIDS was unknown, and many blamed it on the most marginalized groups. But, without knowing that the disease was caused by a virus, it was easy to stigmatize, isolate and blame affected groups. The early approach towards understanding AIDS focused on who was getting infected, rather than the cause and effect of the disease. Epidemiologists saw that AIDS was affecting hemophiliacs, heroin addicts, homosexuals, and Haitians (the 4Hs of HIV) which biased the way people viewed the disease and the populations it first impacted. Infection did not seem to follow logic.
PART 1.3
Too many people were dying from automobile crashes on highways. But people considered these crashes to be “accidents,” or acts of fate for which we could not know the cause. They argued that if we could not know the cause, we could not prevent them. People were not thinking of cause and effect.
PART 2.1
To apply the surveillance and containment strategy, it was necessary to know where the smallpox virus was, which villages had active cases of smallpox. The struggle against smallpox could not be won without knowing where the enemy was and what it was doing. But India did not have accurate surveillance data. Many villages with active cases had not been reported.
PART 2.2
While Guinea worm was widespread in Nigeria and Ghana, the leaders thought Guinea worm impacted only a small number of people and for this reason they were not motivated to do anything to solve the problem. But what government leaders thought were a few hundred cases turned out to be over 650,000 cases.
PART 3.1
Implementing the smallpox surveillance and containment strategy required massive resources, commitment, and coordination. But moving from a traditional strategy, used for over a century and a half with clearly defined roles for every participant, to a new strategy simply seemed too labor intensive and impossible. This required mobilizing and coordinating hundreds of thousands of implementers with a gradual increase in the number of people involved.
PART 3.3
Many different organizations were involved with immunizations brought together by The Task Force for Child Survival starting in 1984. But this coalition fell apart in the 1990s when the agency heads, who had been effective collaborators, turned over. They had to rebuild the coalition that had worked under the auspices of The Task Force.
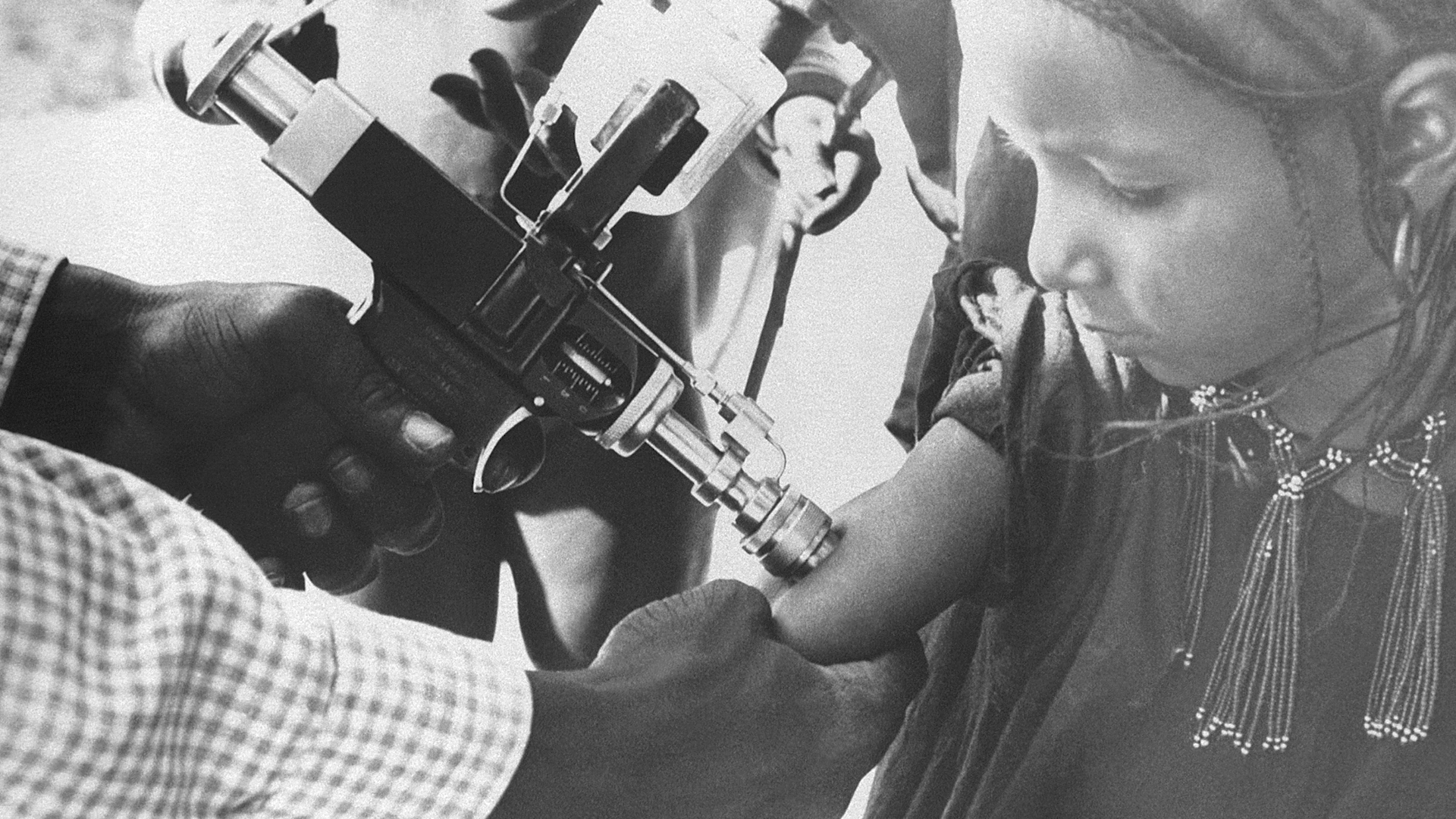
PART 4.1
Mass vaccination was the tried-and-true approach to smallpox eradication. Mass vaccination success was measured by the percentage of the population that was vaccinated, in order to achieve herd immunity. Most countries, WHO and other multilateral organizations were committed to this approach and operationally tied the goals to this strategic approach.
PART 4.2
Women and their babies were dying from complications of home labor and delivery. Nana and her colleagues were pretty sure that they understood the problem. They thought this was happening because when the women went into labor they had no way to get themselves to their local healthcare facility. They thought that transportation to healthcare facilities that was local, affordable, and accessible was needed. Yet even after MAZA implemented motorized tricycles operated by local drivers in the community to transport women to healthcare facilities, the women were not going to the healthcare facilities.
PART 4.3
When HIV first became prominent as a mysterious disease, people had many theories of how it was spread, almost all of them focused on the “immoral and drug-fueled” sexual activities of highly stigmatized groups. They not only held very strong views but they were absolutely certain that they were right. But the public, politicians and scientists were all challenged to rethink their ideas of spread when confronted by reports that the disease could be transmitted by infusing clotting factors from a donor to a patient with hemophilia.
PART 4.4
In the early 2000’s WHO had adopted the ambitious goal of getting 3 million people on antiretroviral medicines by 2005. But some people thought this was too ambitious a goal and that it could never be achieved. Leaders were afraid of making a mistake and being wrong, so they were hesitant to act until they were certain they could achieve their goal. Yet waiting would cause costly delays as the disease raged on, and prevent otherwise ambitious and very important programs from making progress.
PART 5.2
The polio eradication program relied on strong surveillance efforts to inform vaccination efforts. Surveillance teams worldwide constantly searched for cases in which people had limbs that could not be moved and just hung limply, or cases of “flaccid paralysis.”When they found these cases, they would target vaccination to those regions. This was a very effective strategy when polio was widespread, because almost every case of flaccid paralysis was caused by polio. As vaccination coverage increased, cases of paralytic polio plummeted. As cases of flaccid paralysis began to disappear, polio was declared eliminated from many countries and regions. But in many areas polio persisted.
PART 5.3
Infants were dying in rural health centers because they had complications that couldn't be dealt with in those hospitals. Doctors thought that a way to address this would be to transfer them to a larger hospital with more neonatal capacity. But, when the transfer solution was tried, it turned out that more infants were dying. Lives were not being saved. Babies continued to die because the transportation to the secondary or tertiary facilities took so long. The infants could not survive the trip.
PART 5.4
Gun violence takes an extraordinary toll on individuals, families, and communities in the United States. But the NRA has been successful in working through Congress to make sure that much of the critical data for assessing the problem, and finding interventions that work, is not collected, maintained, or made available.
PART 6.1
In the early 1960s, India accounted for nearly 60 percent of the reported smallpox cases in the world. The Indian government had launched the National Smallpox Eradication Program which focused on mass vaccination. By 1966, the Indian government reported approximately 60 million primary vaccinations. Mass vaccination campaigns had become part of the culture, and there was wide trust in this singular approach. However, the number of smallpox cases in India was increasing and India needed a new strategy.
PART 6.2
In Mozambique, there was local distrust of the health clinic. A woman did come into the health clinic to deliver her child but both she and the child died in childbirth. The doctor, Hans Rosling, felt terrible and worried that he would never regain the trust of the people in the surrounding villages. But he learned that it was important for him to return the bodies to the village for a proper burial as a sign of respect for the local culture.
PART 6.3
Gun violence research sought ways to prevent unnecessary gun deaths, disabilities, and anxiety. Many gun owners opposed research by the CDC on gun violence prevention because they believed that the goal of the research was to take their guns away. But the rise of mass school shootings led to a change in perspective because everyone was concerned about the safety of their children.
PART 7.1
In early 1974, smallpox outbreaks were appearing in areas of India that had been smallpox-free for months. After a week of plotting the epidemic with pushpins on hand-drawn maps, a pattern emerged. Each outbreak began with a working-age young man who had returned home to his village. These cases were “importations.” The young men had come from—or traveled through—the bordering state of Bihar. Cases were originating in Tatanagar, the company town of the corporate behemoth, Tata Companies. Tatanagar, a city in the state of Bihar, had no centralized government, and no public health structure in place.
PART 7.2
One of the most challenging things for vaccinations is reaching those who live “at the end of the road”—those who are geographically isolated due to distance or living in hard to access regions. A well-functioning delivery system is one that reaches the patient at the point-of-care. Such a system is essential for adequate access to and availability of vaccines. But, while across Africa, governments and donors are investing billions of dollars to strengthen health systems and make affordable medicines available, government supply chains often struggle to get medicines and supplies through the last mile to the health facilities and to the people who need them most.