PART 1.2
In the early days of HIV/AIDS, AIDS was a mysterious disease. The cause of AIDS was unknown, and many blamed it on the most marginalized groups. But, without knowing that the disease was caused by a virus, it was easy to stigmatize, isolate and blame affected groups. The early approach towards understanding AIDS focused on who was getting infected, rather than the cause and effect of the disease. Epidemiologists saw that AIDS was affecting hemophiliacs, heroin addicts, homosexuals, and Haitians (the 4Hs of HIV) which biased the way people viewed the disease and the populations it first impacted. Infection did not seem to follow logic.
PART 6.2
In Mozambique, there was local distrust of the health clinic. A woman did come into the health clinic to deliver her child but both she and the child died in childbirth. The doctor, Hans Rosling, felt terrible and worried that he would never regain the trust of the people in the surrounding villages. But he learned that it was important for him to return the bodies to the village for a proper burial as a sign of respect for the local culture.
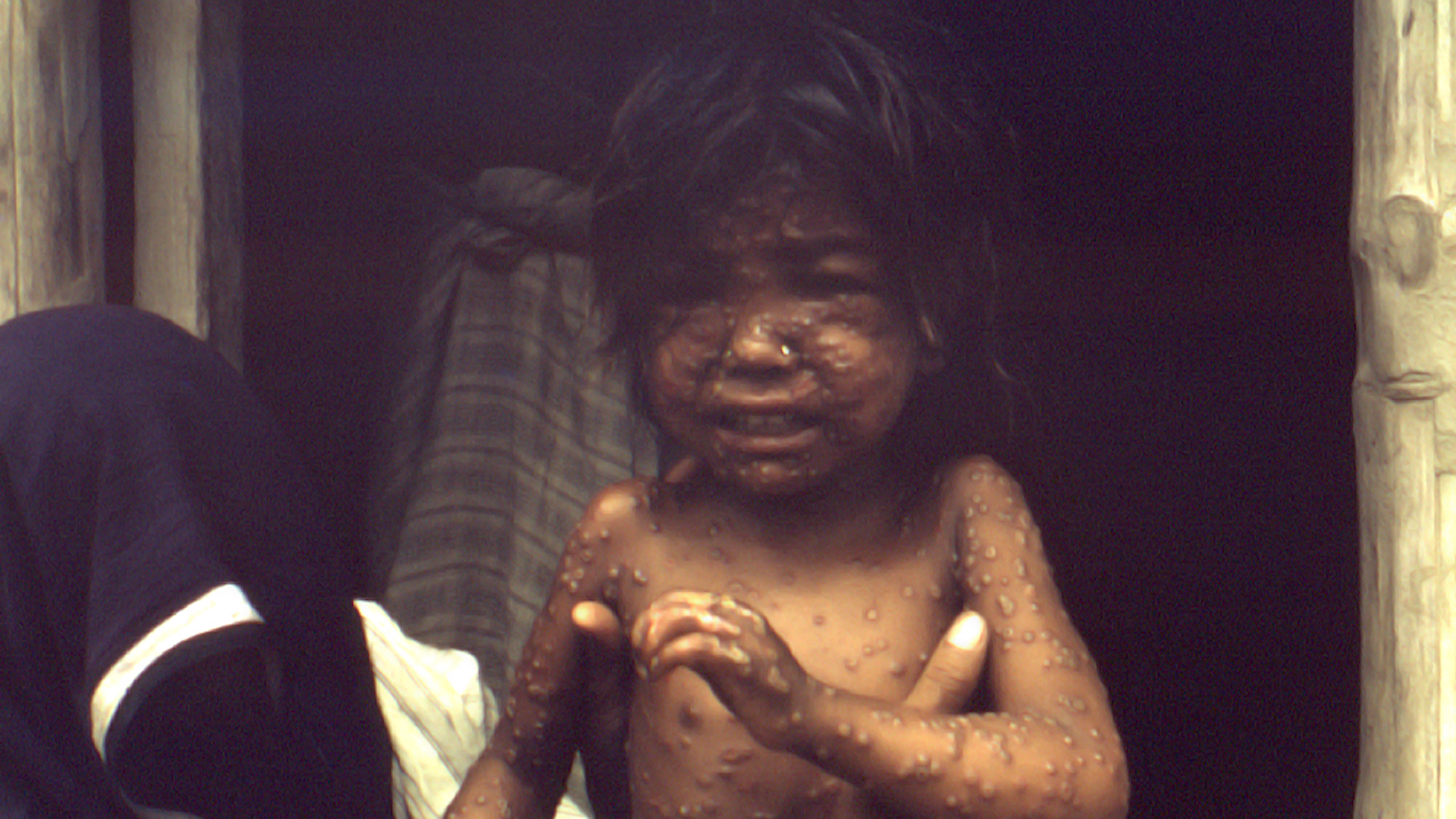
PART 9.1
An effective vaccine for preventing smallpox had been discovered and tested by 1796. And by the 1970’s widespread vaccination resulted in most people in rich countries being vaccinated and almost completely protected. Smallpox was actually eliminated from developed countries in the 1970s. But the burden of smallpox was inequitably distributed. People in some poor countries remained vulnerable and faced high risks of mortality from smallpox. It was within the poorest communities that smallpox was spread.